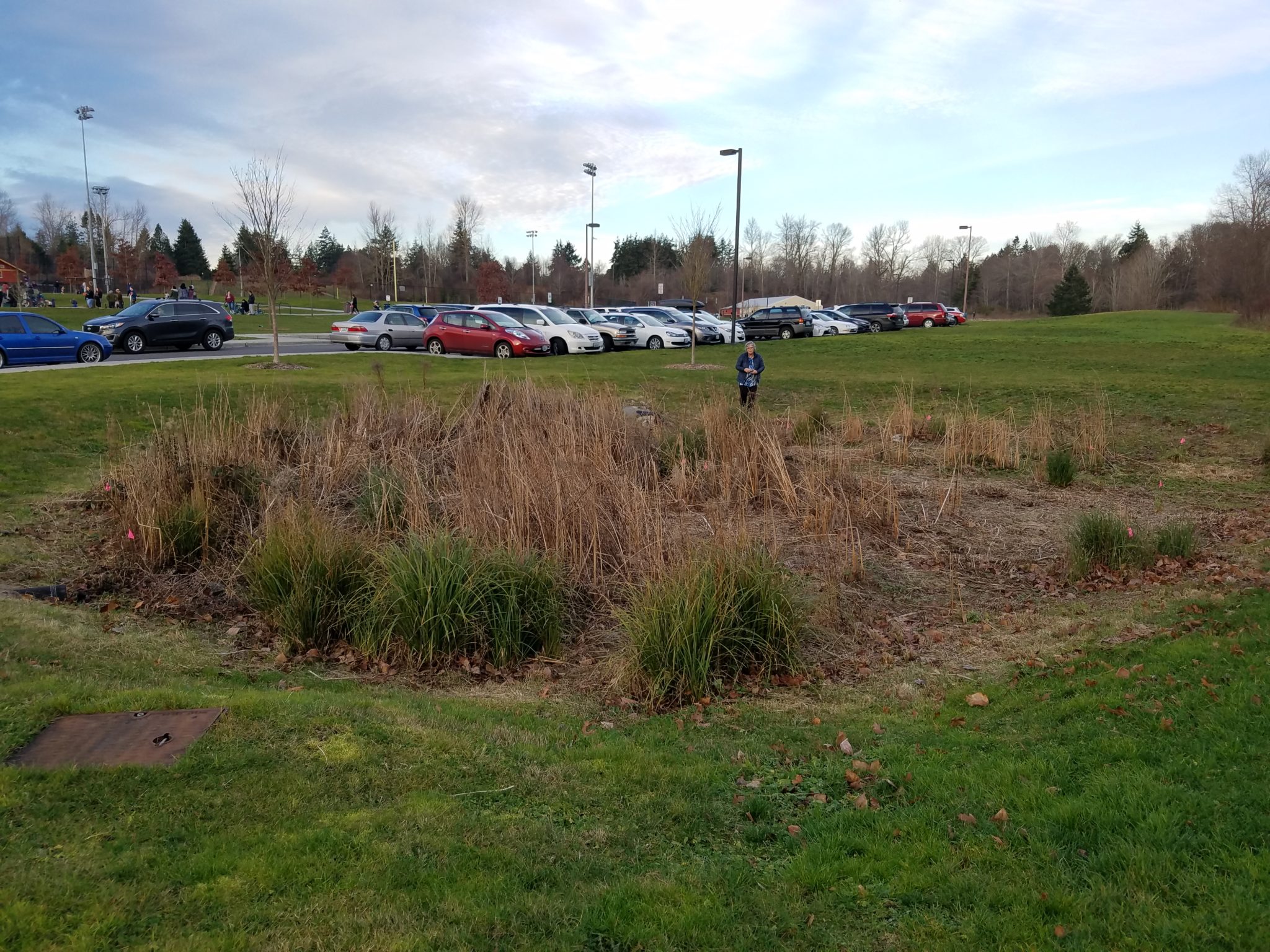
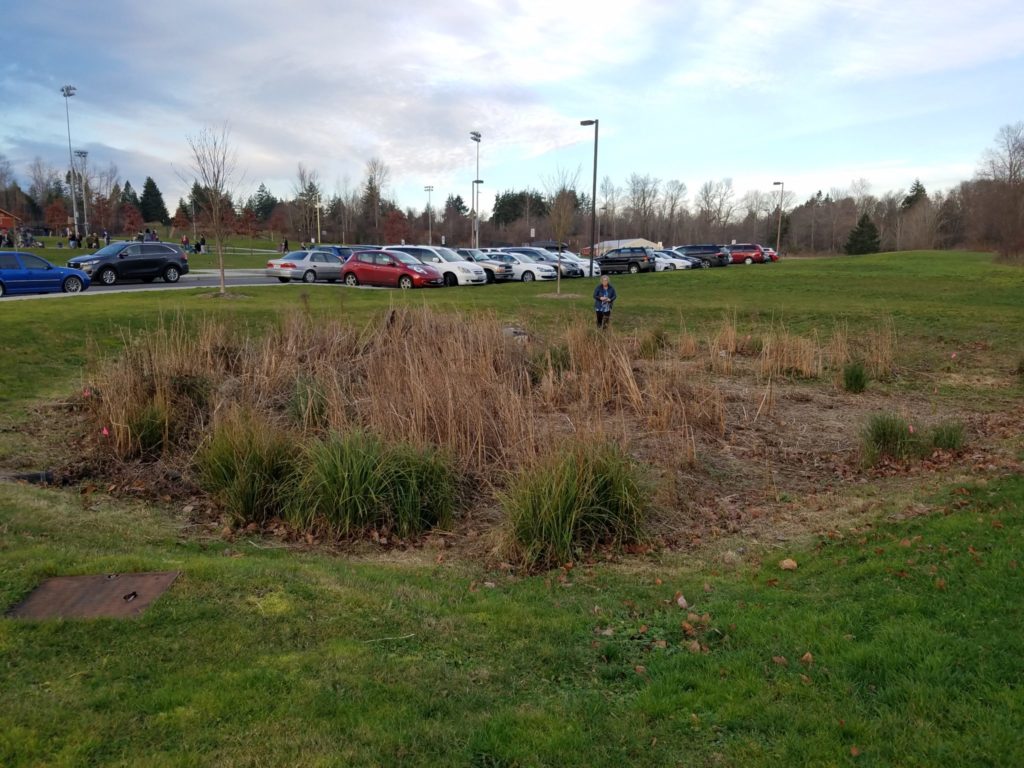
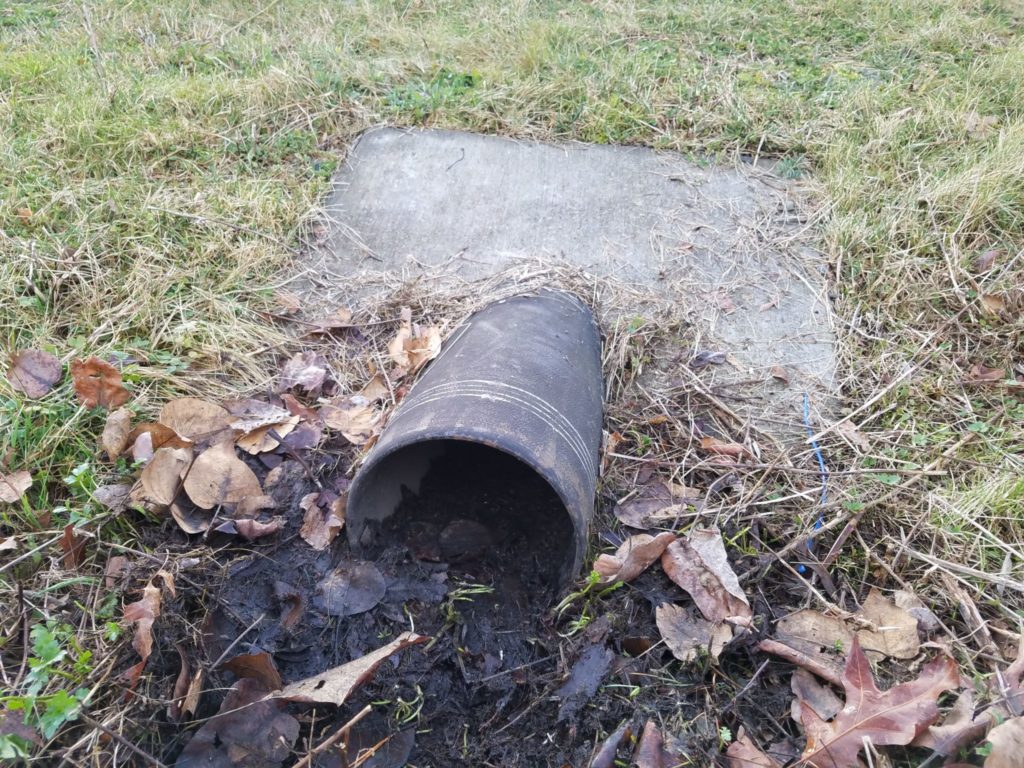
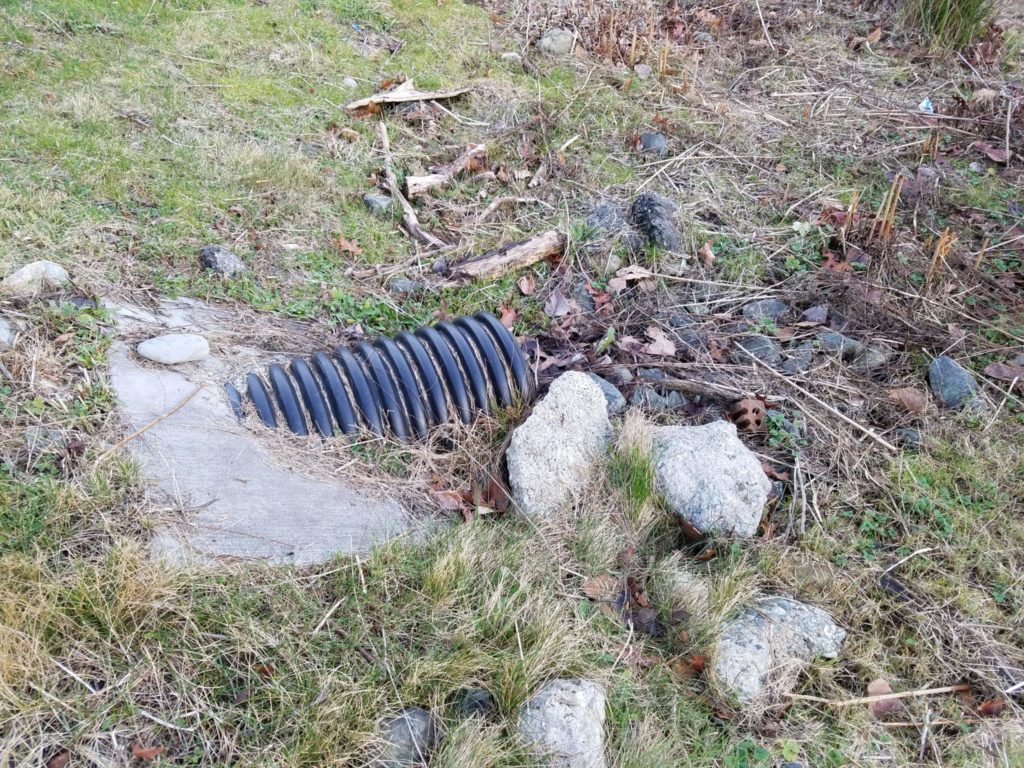
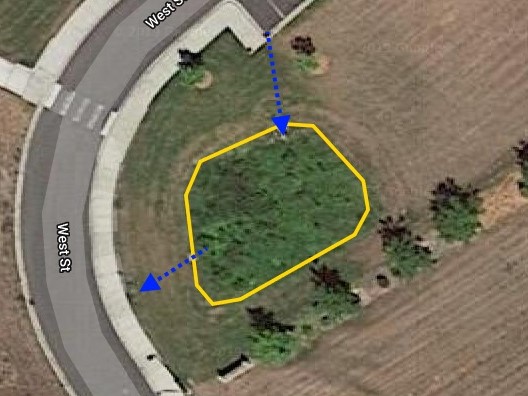
Where is this located? As you enter the park, it lies to the right of the park road.
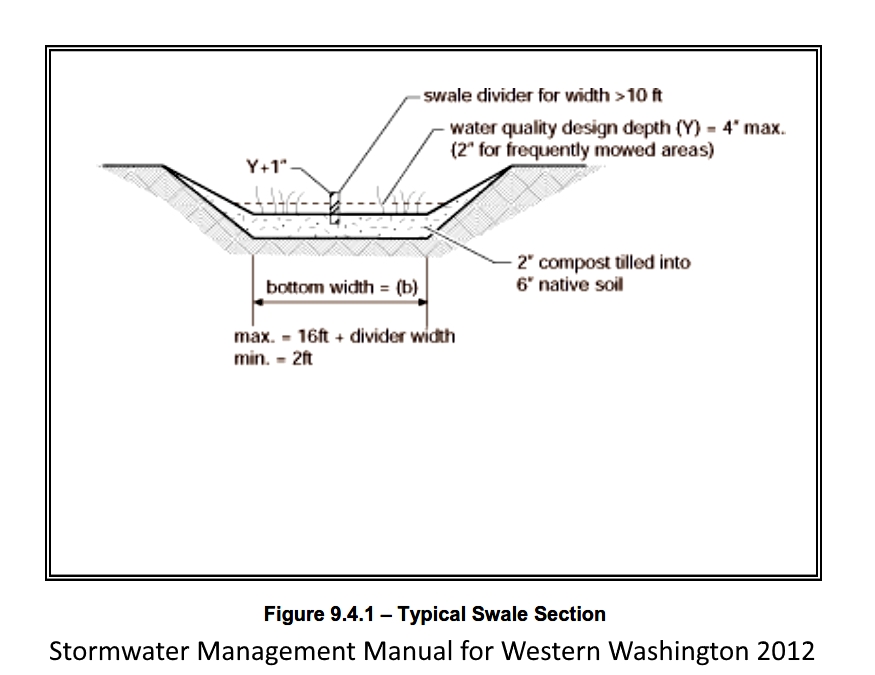
What’s special about this place? The small part of the parking lot is closest to the entry drains to this small engineered rain garden. As runoff slowly makes its way from the inlet to the outlet across the rain garden, plants cause particles to settle and the vegetation and roots take up nutrients and other contaminants. It’s a very effective way to treat polluted runoff in an inexpensive way because the treatment is provided on-site.
image gallery
select any photo to see a slideshow